Turbine Components
The image below demonstrates the components involved in a three bladed Horizontal Axis wind turbine
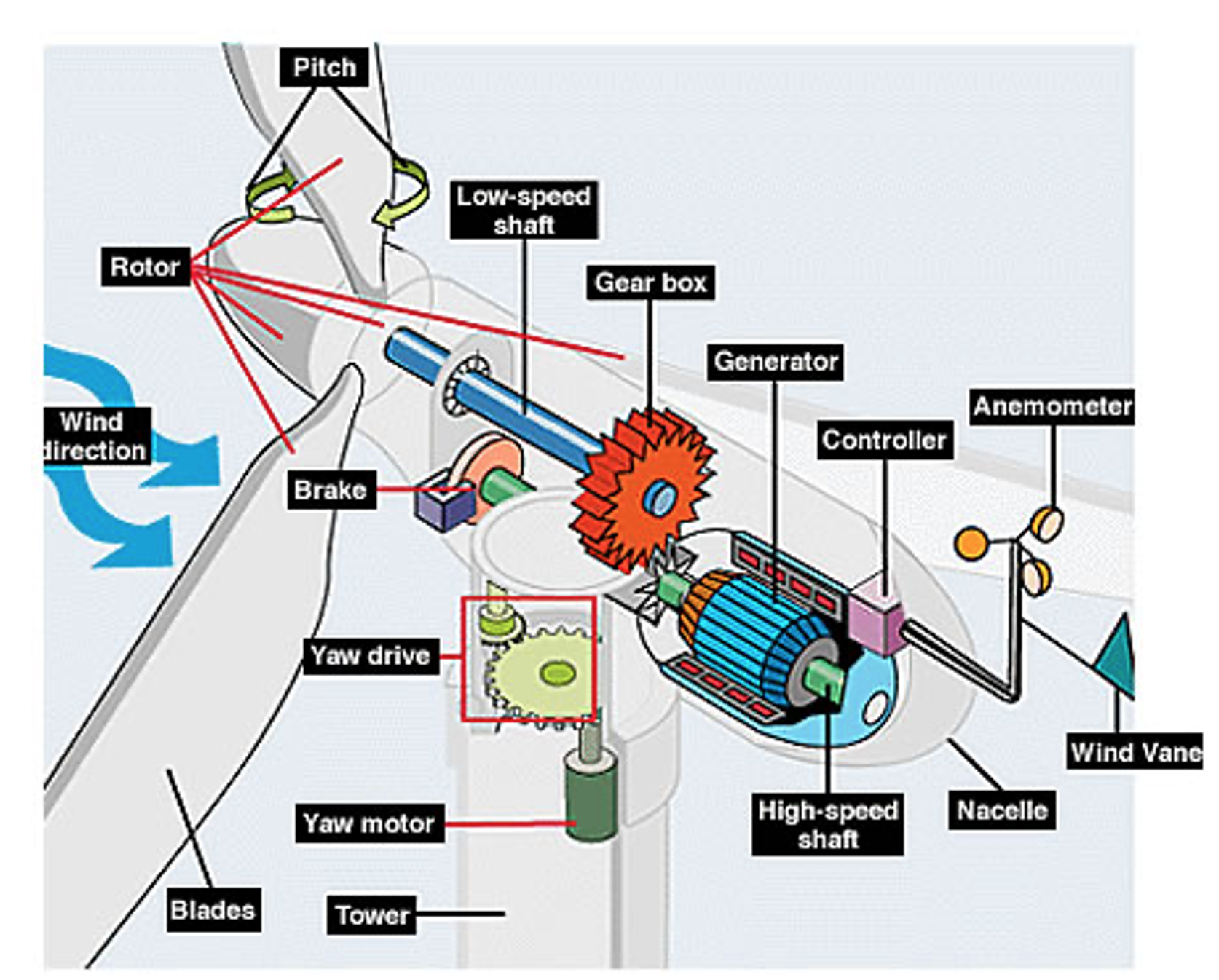
Here are brief descriptions of WT components:
- Rotor: The wind turbine blades and hub together.
- Blades: Extract kinetic energy from the wind and converts it into rotational mechanical shaft energy as a driving torque and wind turbine speed at a certain wind speed.
- Pitch System: Controls the angle of attack of the blades to the wind to control the extraction of kinetic energy and thereby the driving torque and speed.
- Brake: A disc brake to slow down and stop the rotor at cut-out wind speed or in over-speed emergencies.
- Low-speed shaft: Turned by the wind turbine rotor.
- Gearbox: Used to transfer rotational mechanical energy from the low speed shaft to the high speed shaft.
- High-speed shaft: Driven by the gearbox output coupled to the generator and drives the generator.
- Generator: Converts the rotational mechanical shaft energy from the high speed shaft into electrical energy, developing a reaction torque to the high speed shaft.
- Converter: Controls the flow of electrical energy from the generator by adjusting its rotational speed and therefore its reaction torque on the gearbox and wind turbine.
- Controller: Starts up and shuts down the wind turbine at the cut-in and cut-out wind speeds, controls the pitch, converter and yaw system to point the wind turbine into the wind and develop the appropriate reaction torque to the wind turbine at the given wind speed.
- Anemometer: Measures the wind speed and sends the data to the controller to assist in the development of the reaction torque.
- Wind Vane: Measures the wind direction and sends the data to the controller to control the yaw system.
- Nacelle: Housing on the top the tower to yaw into the wind and protect the drive-train assembly, shafts, gearbox, generator and converter.
- Yaw drive: Used to control the nacelle to face the wind as wind direction changes.
- Yaw motors: Power the yaw drive.
- Tower: Supports the nacelle at an appropriate height, as wind speed increases with height, taller towers enable WTs to capture more energy and generate more electricity.
There are a significant number of large, horizontal axis, WT manufacturers in the world, > 50 and their WT designs vary from manufacturer to manufacturer. However, the sub-assemblies described above are common to almost all manufacturers and this gives confidence in taking a common approach to all WTs.